Chef DSM role-based access control
Note
Chef DSM uses organizations, groups, and users to define role-based access control:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
An organization is the top-level entity for role-based access control in Chef DSM. Each organization contains the default groups (admins, clients, and users), at least one user and at least one node (on which the Chef Infra Client is installed). Chef DSM supports multiple organizations. Chef DSM includes a single default organization that’s defined during setup. Additional organizations can be created after the initial setup and configuration of Chef DSM. | |
| A group is used to define access to object types and objects in Chef DSM and also to assign permissions that determine what types of tasks are available to members of that group who are authorized to perform them. Groups are configured per-organization. Individual users who are members of a group will inherit the permissions assigned to the group. Chef DSM includes the following default groups: admins, clients, and users. | |
A user is any non-administrator human being who will manage data that’s uploaded to Chef DSM from a workstation. Chef DSM includes a single default user that’s defined during setup and is automatically assigned to the admins group. | |
| A client is an actor that has permission to access Chef DSM. A client is most often a node (on which the Chef Infra Client runs), but is also a workstation (on which knife runs), or some other machine that’s configured to use the Chef DSM API. Each request to Chef DSM that’s made by a client uses a private key for authentication that must be authorized by the public key on Chef DSM. |
When a user makes a request to Chef DSM using the Chef DSM API, permission to perform that action is determined by the following process:
- Check if the user has permission to the object type
- If no, recursively check if the user is a member of a security group that has permission to that object
- If yes, allow the user to perform the action
Organizations
A single instance of Chef DSM can support many organizations. Each organization has a unique set of groups and users. Each organization manages a unique set of nodes, on which a Chef Infra Client is installed and configured so that it may interact with a single organization on Chef DSM.
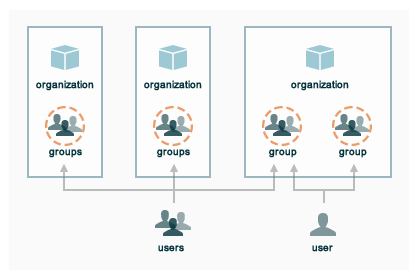
A user may belong to multiple organizations under the following conditions:
- Role-based access control is configured per-organization
- For a single user to interact with Chef DSM using knife from the same chef-repo, that user may need to edit their config.rb file prior to that interaction
Using multiple organizations within Chef DSM ensures that the same toolset, coding patterns and practices, physical hardware, and product support effort is being applied across the entire company, even when:
- Multiple product groups must be supported—each product group can have its own security requirements, schedule, and goals
- Updates occur on different schedules—the nodes in one organization are managed completely independently from the nodes in another
- Individual teams have competing needs for object and object types—data bags, environments, roles, and cookbooks are unique to each organization, even if they share the same name
Permissions
Permissions are used in Chef DSM to define how users and groups can interact with objects on the server. Permissions are configured for each organization.Object Permissions
Chef DSM includes the following object permissions:
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
| Delete | Use the Delete permission to define which users and groups may delete an object. This permission is required for any user who uses the knife [object] delete [object_name] argument to interact with objects on Chef DSM. |
| Grant | Use the Grant permission to define which users and groups may configure permissions on an object. This permission is required for any user who configures permissions using the Administration tab in the Chef management console. |
| Read | Use the Read permission to define which users and groups may view the details of an object. This permission is required for any user who uses the knife [object] show [object_name] argument to interact with objects on Chef DSM. |
| Update | Use the Update permission to define which users and groups may edit the details of an object. This permission is required for any user who uses the knife [object] edit [object_name] argument to interact with objects on Chef DSM and for any Chef Infra Client to save node data to Chef DSM at the conclusion of a Chef Infra Client run. |
Global Permissions
Chef DSM includes the following global permissions:
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
| Create | Use the Create global permission to define which users and groups may create the following server object types: cookbooks, data bags, environments, nodes, roles, and tags. This permission is required for any user who uses the knife [object] create argument to interact with objects on Chef DSM. |
| List | Use the List global permission to define which users and groups may view the following server object types: cookbooks, data bags, environments, nodes, roles, and tags. This permission is required for any user who uses the knife [object] list argument to interact with objects on Chef DSM. |
These permissions set the default permissions for the following Chef DSM object types: clients, cookbooks, data bags, environments, groups, nodes, roles, and sandboxes.
Client Key Permissions
Note
Keys should have DELETE, GRANT, READ and UPDATE permissions.
Use the following code to set the correct permissions:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require 'chef/knife'
#previously knife.rb
Chef::Config.from_file(File.join(Chef::Knife.chef_config_dir, 'knife.rb'))
rest = Chef::ServerAPI.new(Chef::Config[:chef_server_url])
Chef::Node.list.each do |node|
%w(read update delete grant).each do |perm|
ace = rest.get("nodes/#{node[0]}/_acl")[perm]
ace['actors'] << node[0] unless ace['actors'].include?(node[0])
rest.put("nodes/#{node[0]}/_acl/#{perm}", perm => ace)
puts "Client \"#{node[0]}\" granted \"#{perm}\" access on node \"#{node[0]}\""
end
end
Save it as a Ruby script—chef_server_permissions.rb, for
example—in the .chef/scripts directory located in the chef-repo, and
then run a knife command similar to:
knife exec chef_server_permissions.rb
Knife ACL
The knife plugin knife-acl provides
a fine-grained approach to modifying permissions, by wrapping API calls
to the _acl endpoint and makes such permission changes easier to
manage.
Groups
Chef DSM includes the following default groups:
| Group | Description |
|---|---|
admins | The admins group defines the list of users who have administrative rights to all objects and object types for a single organization. |
clients | The clients group defines the list of nodes on which a Chef Infra Client is installed and under management by Chef. Think of this permission as the non-human actors—Chef Infra Client, in nearly every case—that get data from, and/or upload data to Chef DSM. Newly-created Chef Infra Client instances are added to this group automatically. |
public_key_read_access | The public_key_read_access group defines which users and clients have read permissions to key-related endpoints in the Chef DSM API. |
users | The users group defines the list of users who use knife to interact with objects and object types. Think of this permission as all the non-admin human actors who work with data that’s uploaded to or downloaded from the Chef DSM. |
Example Default Permissions
The following sections show the default permissions assigned by the Chef DSM to the admins, billing_admins, clients, and users
groups.
Note
create,
delete, grant, read, and update permission to that object.admins
The admins group is assigned the following:
| Group | Create | Delete | Grant | Read | Update |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| admins | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| clients | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| users | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
billing_admins
The billing_admins group is assigned the following:
| Group | Create | Delete | Read | Update |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| billing_admins | no | no | yes | yes |
clients
The clients group is assigned the following:
| Object | Create | Delete | Read | Update |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| clients | no | no | no | no |
| cookbooks | no | no | yes | no |
| cookbook_artifacts | no | no | yes | no |
| data | no | no | yes | no |
| environments | no | no | yes | no |
| nodes | yes | no | yes | no |
| organization | no | no | yes | no |
| policies | no | no | yes | no |
| policy_groups | no | no | yes | no |
| roles | no | no | yes | no |
| sandboxes | no | no | no | no |
public_key_read_access
The public_key_read_access group controls which users and clients have
read permissions to the following endpoints:
- GET /clients/CLIENT/keys
- GET /clients/CLIENT/keys/KEY
- GET /users/USER/keys
- GET /users/USER/keys/
By default, the public_key_read_access assigns all members of the
users and clients group permission to these endpoints:
| Group | Create | Delete | Grant | Read | Update |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| admins | no | no | no | no | no |
| clients | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| users | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
users
The users group is assigned the following:
| Object | Create | Delete | Read | Update |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| clients | no | yes | yes | no |
| cookbooks | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| cookbook_artifacts | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| data | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| environments | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| nodes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| organization | no | no | yes | no |
| policies | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| policy_groups | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| roles | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| sandboxes | yes | no | no | no |
chef-validator
Every request made by Chef Infra Client to the Chef DSM must be an authenticated request using the Chef DSM API and a private key. When Chef Infra Client makes a request to the Chef DSM, Chef Infra Client authenticates each request using a private key located in/etc/chef/client.pem.The chef-validator is allowed to do the following at the start of a Chef
Infra Client run. After the Chef Infra Client is registered with Chef DSM, that Chef Infra Client is added to the clients group:
| Object | Create | Delete | Read | Update |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| clients | yes | no | no | no |
Manage organizations
For organization management tasks in Chef Declarative State Management (DSM) Service, use the knife org commands.